Japanese architecture (日本建築, Nihon kenchiku ) has traditionally been typified by wooden structures, elevated slightly off the groun...
Manga
Manga (漫ç"», Manga ) are comics created in Japan, or by Japanese creators in the Japanese language, conforming to a style developed ...
Japanese aesthetics
The modern study of Japanese aesthetics only started a little over two hundred years ago in the West. The Japanese aesthetic is a set of an...
Culture of Japan
The culture of Japan has evolved greatly over the millennia, from the country's prehistoric JÅmon period, to its contemporary hybrid c...
Career woman
A career woman (ã‚ャリアウーマン, kyariaÅ«man ) sometimes career girl , is a Japanese term for a Japanese woman, married or not, wh...
Women in Japan
After World War II, the dominant cultural template for the role of a Japanese woman has been that of the "office lady (OL)" , who...
Smoking in Japan
Smoking in Japan , though historically less restricted by law than in many other nations, has significantly changed in recent years. Tobacco...
Sexuality in Japan
Sexuality in Japan has developed separately from mainland Asia, as Japan did not adopt the Confucian view of marriage. Monogamy in marriage...
Religion in Japan
Religion in Japan is dominated by Shinto, which is the ethnic religion of the Japanese people, and by Buddhist schools and organisations. A...
Languages of Japan
The oral languages spoken by the native peoples of the insular country of Japan at present and during recorded history belong to either of t...
Housing in Japan
Housing in Japan includes modern and traditional styles. Two patterns of residences are predominant in contemporary Japan: the single-famil...
Gambling in Japan
Gambling in Japan is generally banned by the Criminal Code chapter 23; however, there are several exceptions, including betting on horse ra...
Etiquette in Japan
The code of etiquette in Japan governs the expectations of social behavior in the country and is considered very important. Like many socia...
Education in Japan
In Japan , education is compulsory at the elementary and lower secondary levels. Most students attend public schools through the lower seco...
Demographics of Japan
The demographic features of the population of Japan include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic...
Crime in Japan
Crime in Japan is lower than in all other industrialized countries. History Yakuza The yakuza had existed in Japan well before th...
Japanese yen
The Japanese yen (円 or åœ", en , symbol: Â¥ ; code: JPY ) is the official currency of Japan. It is the third most traded currency in...
Transport in Japan
Transportation in Japan is modern and highly developed. Japan's transportation sector stands out for its energy efficiency: it uses les...
Solar power in Japan
Solar power in Japan has been expanding since the late 1990s. The country is a leading manufacturer of solar panels and ranks 4th in the wo...
Energy in Japan
Energy in Japan refers to energy and electricity production, consumption, import and export in Japan. The country's primary energy cons...
Labor market of Japan
The labor force in Japan numbered 65.9 million people in 2010, which was 59.6% of the population of 15 years old and older, and amongst the...
International rankings of Japan
The following are international rankings of Japan. Cities Tokyo-Yokohama, Mercer Human Resource Consulting: Most expensive cities 20...
Bank of Japan
The Bank of Japan (日本銀行, Nippon GinkŠ, BOJ , JASDAQ: 8301) also known as Nippon Ginko , is the central bank of Japan. The Bank is...
Agriculture, forestry, and fishing in Japan
Agriculture, forestry, and fishing form the primary sector of industry of the Japanese economy, together with the Japanese mining industry,...
Economy of Japan
The economy of Japan is the third largest in the world by nominal GDP, the fourth largest by purchasing power parity and is the world'...
Deputy Prime Minister of Japan
The Deputy Prime Minister of Japan (副ç·ç†, Fuku-sÅri ) is a senior member of the Cabinet of Japan. The office of the Deputy Prime Mini...
List of Prime Ministers of Japan
This is a list of Prime Ministers of Japan , including those of the Empire of Japan, from when the first Japanese prime minister (in the mod...
Prime Minister of Japan
The Prime Minister of Japan (内閣ç·ç†å¤§è‡£, Naikaku-sÅri-daijin ) is the head of government of Japan. He is appointed by the Emperor ...
Ministries of Japan
The most influential part of the executive of the Japanese government are the ministries. In postwar politics, the posts of ministers have b...
Foreign policy of Japan
The primary responsibility for the Japanese foreign policy , as determined by the 1947 constitution, is exercised by the cabinet and subject...
Monetary and fiscal policy of Japan
Monetary policy pertains to the regulation, availability, and cost of credit, while fiscal policy deals with government expenditures, taxe...
Cabinet of Japan
The Cabinet of Japan (内閣, Naikaku ) is the executive branch of the government of Japan. It consists of the Prime Minister, who is appoi...
Government of Japan
The government of Japan is a constitutional monarchy whereby the power of the Emperor is limited and is relegated primarily to ceremonial d...
Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force
The Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (海上自衛隊, KaijŠJieitai ), or JMSDF , is the naval branch of the Japan Self-Defense Forces, ...
Japan Ground Self-Defense Force
The Japan Ground Self-Defense Force ( JGSDF ; Japanese: 陸上自衛隊;, RikujŠJieitai ), is the main branch of the Japan Self-Defense F...
Japan Air Self-Defense Force
The Japan Air Self-Defense Force (航空自衛隊, KÅkÅ« Jieitai ), or JASDF , is the aviation branch of the Japan Self-Defense Forces r...
Japan Self-Defense Forces
The Japan Self-Defense Forces (自衛隊, Jieitai ), or JSDF , occasionally referred to as JSF or SDF , are the unified military forces of...
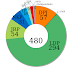
List of political parties in Japan
This article lists political parties in Japan . Major parties Other parties currently represented in the national Diet Legal status ...
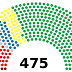
House of Representatives (Japan)
The House of Representatives (衆è°é™¢, ShÅ«giin ) is the lower house of the National Diet of Japan. The House of Councillors is the upp...